Innovative Water Separation Techniques: Revolutionizing Dredge Sludge Disposal
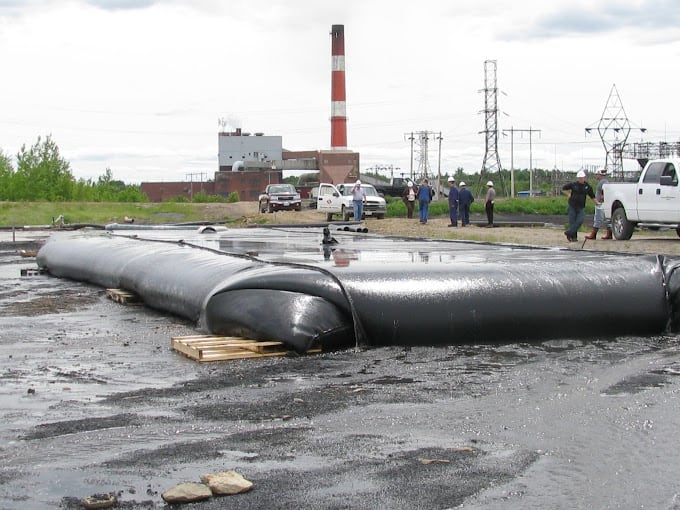
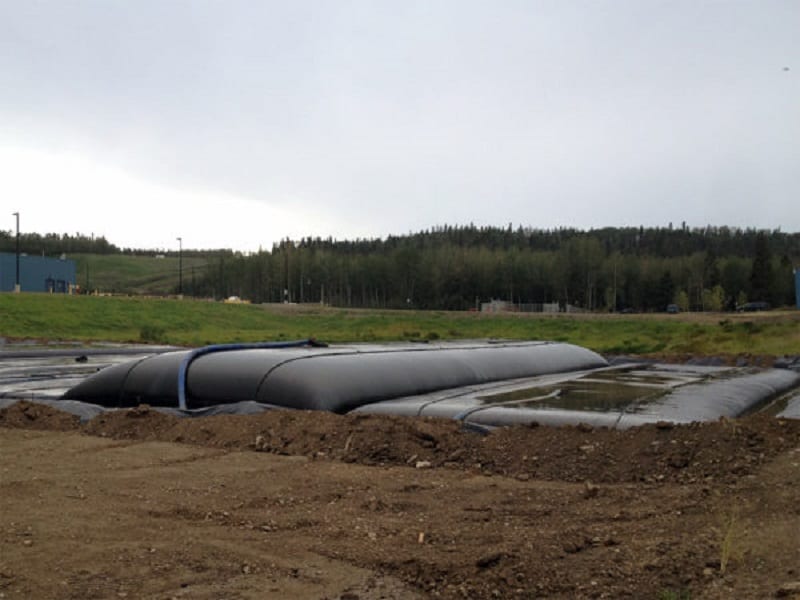
In the ever-evolving field of environmental management, the disposal of dredge sludge poses a significant challenge. Traditional methods of handling sludge are often inefficient and costly. However, recent advancements in water separation techniques have revolutionized the way dredge sludge is managed, offering more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solutions. This blog explores these innovative techniques, highlighting the role of dewatering bags in transforming dredge sludge disposal. Understanding Dredge Sludge Disposal Dredging is a critical process for maintaining waterways, harbors, and marinas, ensuring they remain navigable and free of silt and debris. However, the sludge generated from dredging activities requires proper disposal to prevent environmental contamination. Traditional disposal methods often involve transporting the sludge to landfills or containment areas, which can be both costly and environmentally damaging. The Role of Water Separation Techniques Water separation techniques have emerged as a game-changer in the management of dredge sludge. These methods focus on efficiently separating water from the sludge, reducing its volume and making it easier to handle and dispose of. By minimizing the water content, these techniques significantly lower transportation and disposal costs while mitigating environmental impact. Key Water Separation Techniques Centrifugation How it Works: Centrifugation involves spinning the sludge at high speeds to separate water from solid particles. The centrifugal force pushes the solids to the outer edge of the container, allowing water to be drained away. Advantages: This technique is highly efficient and can handle large volumes of sludge. It is also effective in reducing the water content to very low levels. Geotextile Dewatering Bags How it Works: Dewatering bags, made from durable geotextile fabric, are filled with dredge sludge. Water gradually drains through the fabric, leaving the solid particles behind. The bags can be